MUTATIONS BIOLOGY HONORS WHAT IS A MUTATION A Biology Diagrams These complexes exert their regulatory function by phosphorylation of key proteins involved in cell cycle transitions, such as the product encoded by the retinoblastoma gene (pRB). Mutations and overexpression of cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases, mainly cyclin D1 and Cdk4, have been reported and proposed to be oncogenic events.

The results indicated that the cancer types can be classified into two major groups based on the magnitude of gene expression changes related to the cell cycle and cell proliferative activity caused by TP53 mutations. Furthermore, there was no distinct difference in the effects of GOF and non-GOF mutations on the gene expression profile of the

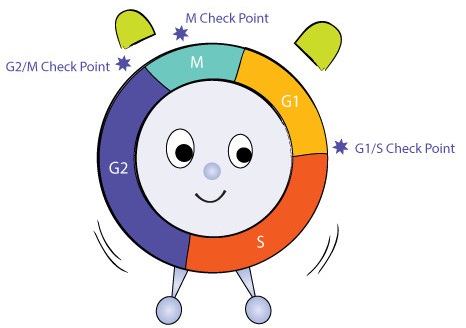
4.10: Mutation Effects Biology Diagrams
Cancer-associated mutations that perturb cell cycle control allow continuous cell division chiefly by compromising the ability of cells to exit the cell cycle. recapitulates the effect of

Many other mutations have no effect on the organism because they are repaired beforeprotein synthesis occurs. Cells have multiple repair mechanisms to fix mutations in DNA. It is generally caused by mutations in genes that regulate the cell cycle. Because of the mutations, cells with damaged DNA are allowed to divide without limits.

Different impacts of TP53 mutations on cell cycle Biology Diagrams
Cancer is a systemic manifestation of aberrant cell cycle activity and dysregulated cell growth. Genetic mutations can determine tumor onset by either augmenting cell division rates or restraining normal controls such as cell cycle arrest or apoptosis. As a result, tumor cells not only undergo uncontrolled cell division but also become compromised in their ability to exit the cell cycle